What can a cook in Italy teach a mechanic in India?
Action Recognition Generalisation Over Scenarios and Locations
Motivation: the same action, for example "cut", can be performed very differently based on the scenario and the geographical location in which it is performed.
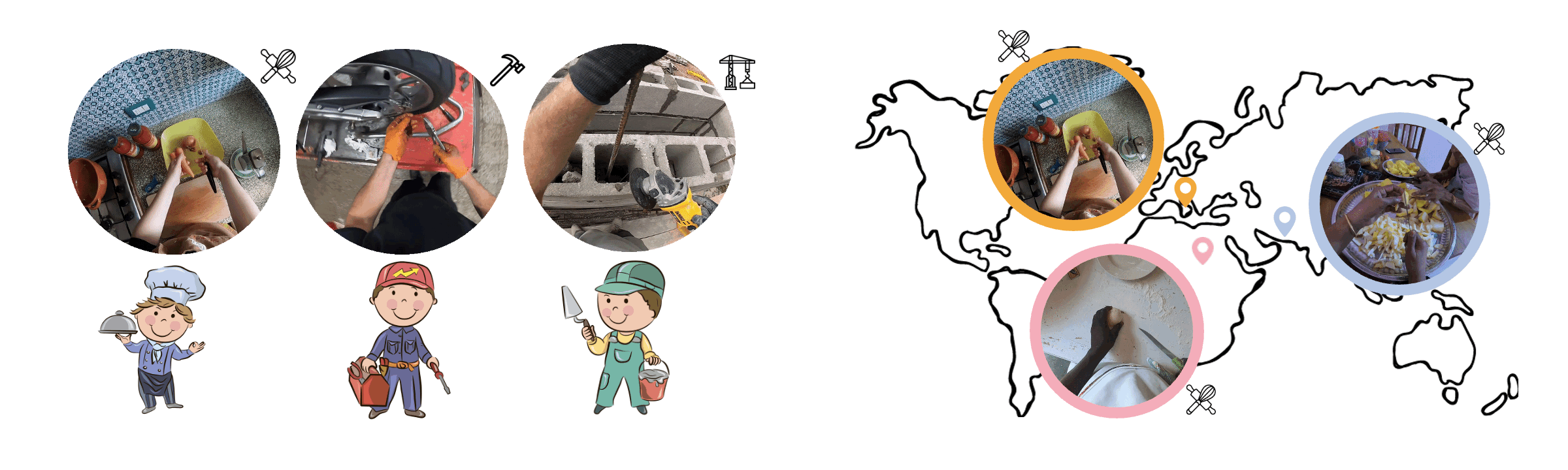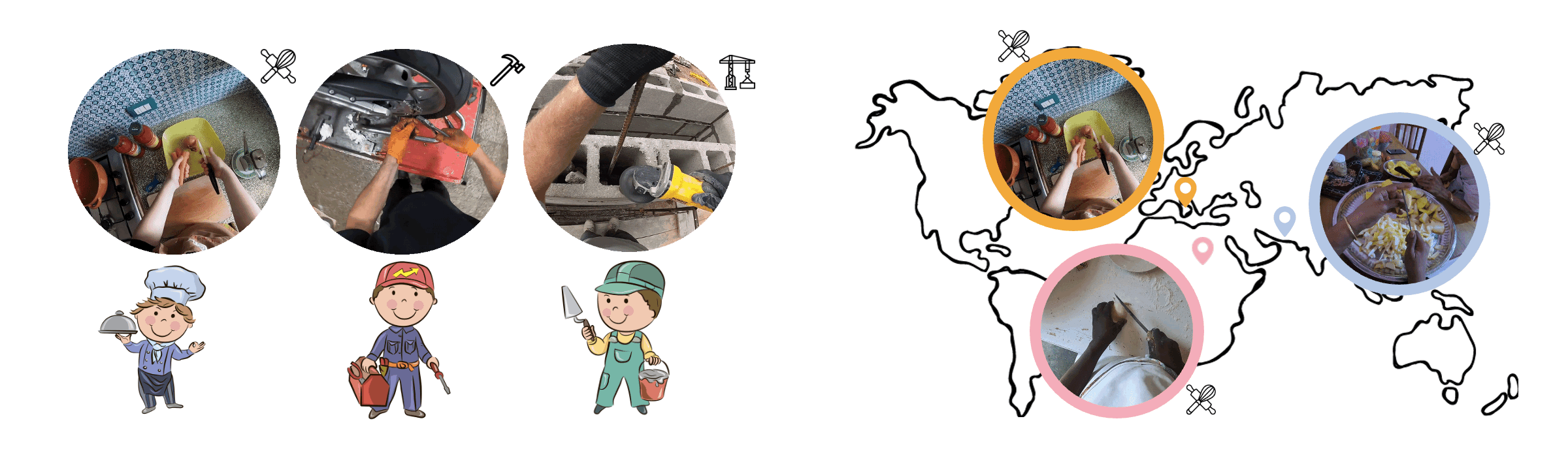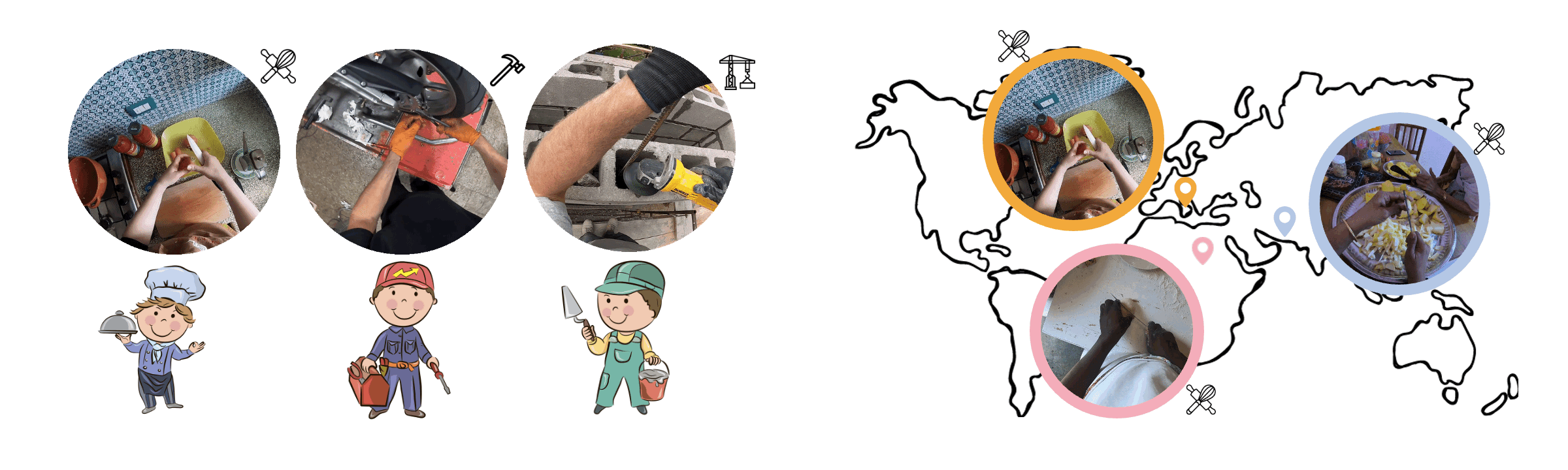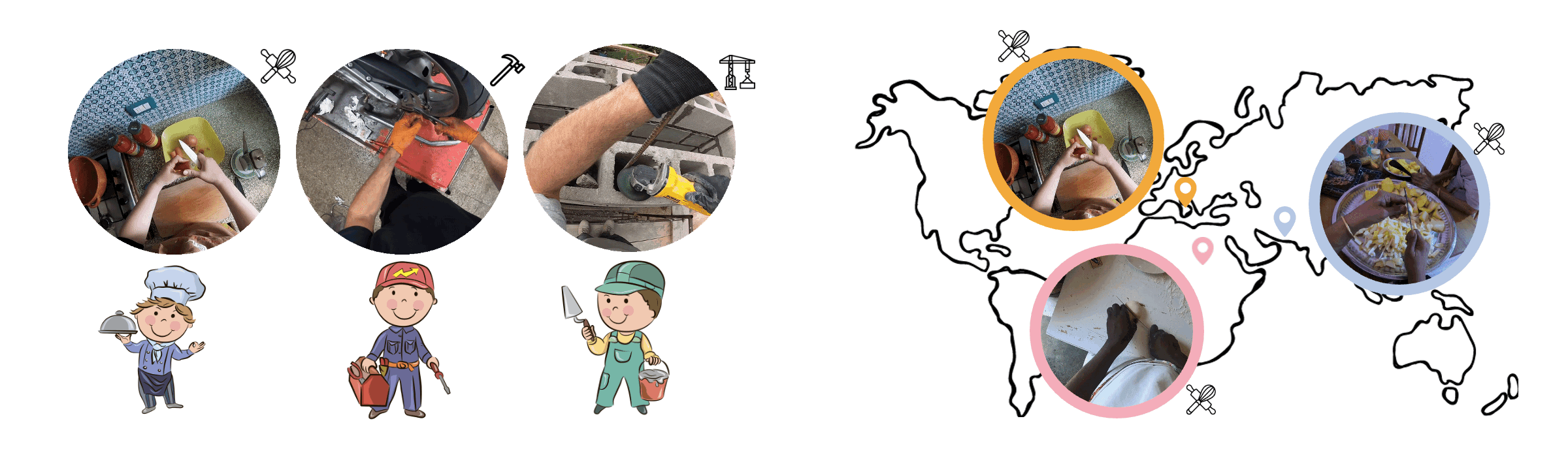

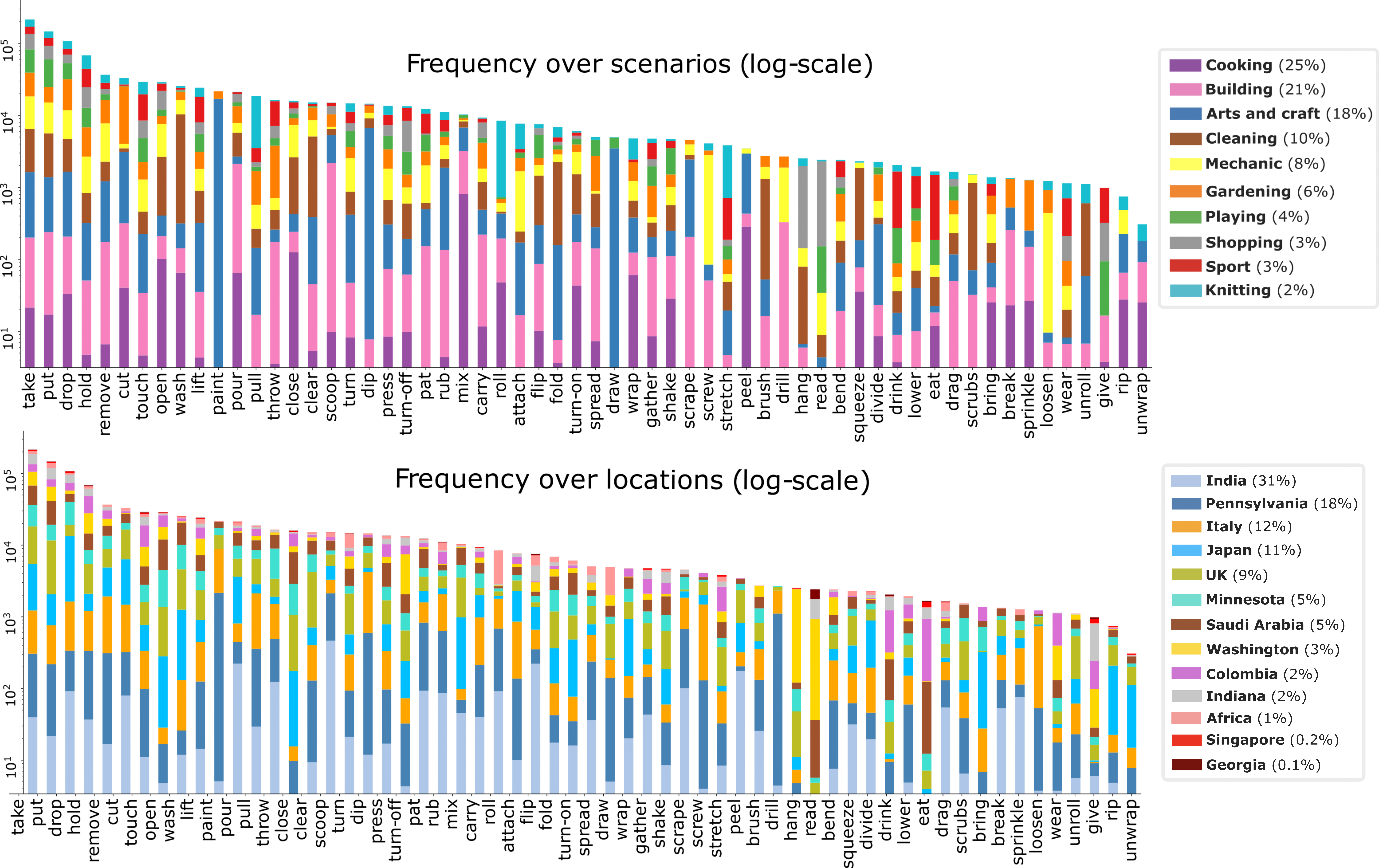
Abstract: We propose and address a new generalisation problem: can a model trained for action recognition successfully classify actions when they are performed within a previously unseen scenario and in a previously unseen location? To answer this question, we introduce the Action Recognition Generalisation Over scenarios and locations dataset (ARGO1M), which contains 1.1M video clips from the large-scale Ego4D dataset, across 10 scenarios and 13 locations. We demonstrate recognition models struggle to generalise over 10 proposed test splits, each of an unseen scenario in an unseen location. We thus propose CIR, a method to represent each video as a Cross-Instance Reconstruction of videos from other domains. Reconstructions are paired with text narrations to guide the learning of a domain generalisable representation. We provide extensive analysis and ablations on ARGO1M that show CIR outperforms prior domain generalisation works on all test splits.
Dataset: ARGO1M
1. Sign EGO4D License Agreement and get AWS access credentials;
2. Download the AWS CLI;
3. Download the dataset from AWS servers.
Follow details in ARGO1M.
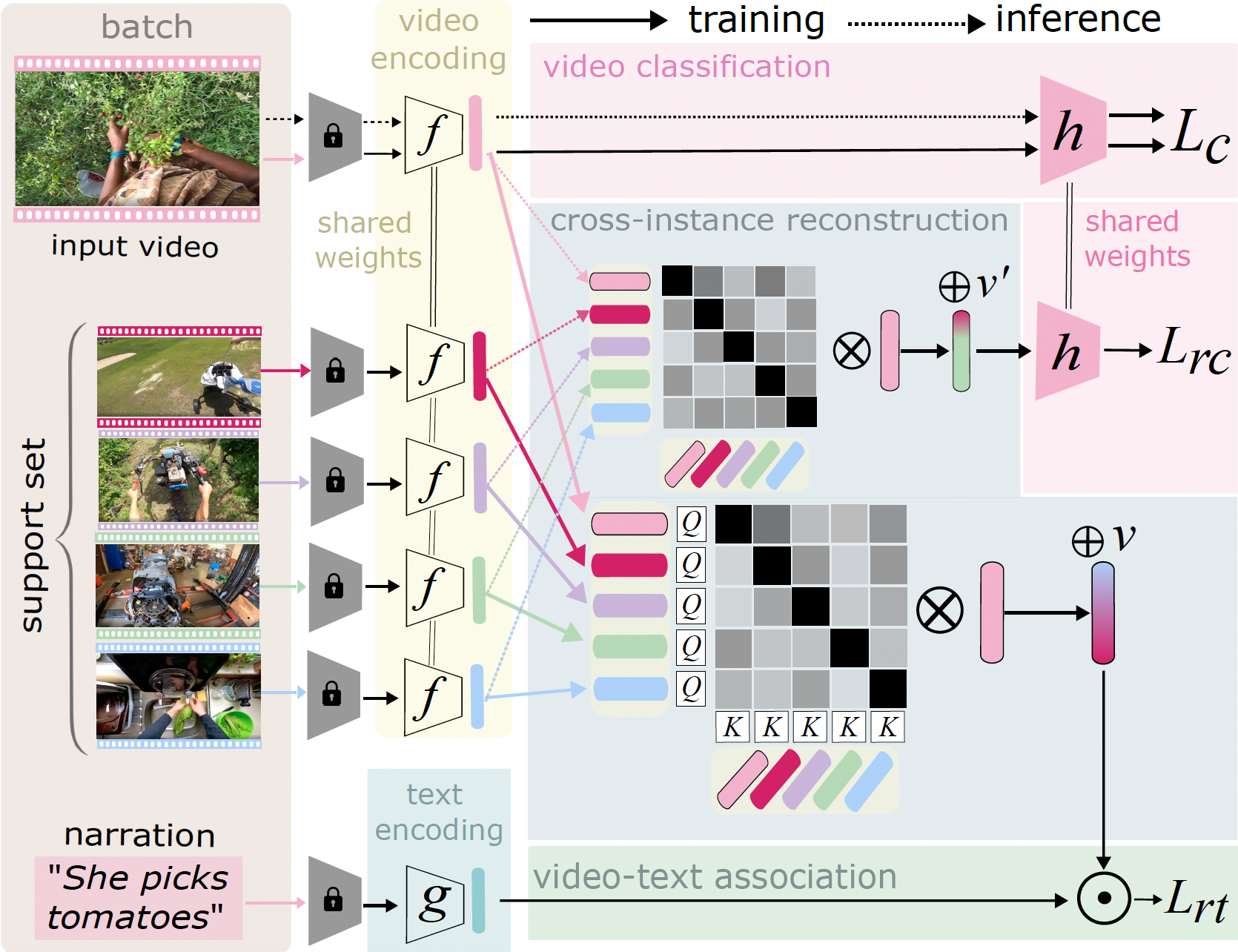
Method: CIR

CIR visualisation
We visualise reconstructed instances from the training set by CIR and their (top-5) support set. On the top left, we show the query video clip, along with the corresponding narration (top of the video), scenario (icon on the top-right of the video), and location (pin on the top-right map). On the bottom row, we show the j-th support video clip, along with its narration (top of the video), scenario (icon below) and location (pin on the map).Full video
YouTube
|
Acknowledgements
Research at Bristol is supported by
EPSRC Fellowship UMPIRE (EP/T004991/1) and EPSRC
Program Grant Visual AI (EP/T028572/1). This project ac-
knowledges the use of University of Bristol’s Blue Crystal 4
(BC4) HPC facilities. We also acknowledge travel support
from ELISE (GA no 951847).